Incoterms, or International Commercial Terms, are a set of standardized trade terms that are used to establish the obligations, costs, and risks between buyers and sellers in international trade transactions. They were first introduced by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) in 1936, and have been updated several times since then to reflect changes in global trade practices.
There are currently 11 Incoterms, each denoted by a three-letter code, and they can be divided into two categories: those that are appropriate for any mode of transportation (known as the “E” terms) and those that are specifically designed for sea and inland waterway transport (known as the “F” terms).
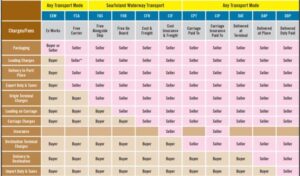
The following is an overview of each Incoterm:
EXW (Ex Works): Under this term, the seller makes the goods available at their premises, and the buyer is responsible for all costs and risks associated with the transportation of the goods from the seller’s premises to the final destination.
FCA (Free Carrier): Under this term, the seller is responsible for delivering the goods to a carrier or another party specified by the buyer, at a named place. The seller is responsible for loading the goods onto the transport vehicle.
CPT (Carriage Paid To): Under this term, the seller is responsible for delivering the goods to a carrier or another party specified by the buyer, at a named place. The seller is responsible for the cost of transportation to the named place.
CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid To): Under this term, the seller is responsible for delivering the goods to a carrier or another party specified by the buyer, at a named place. The seller is responsible for the cost of transportation to the named place, as well as insurance for the goods during transit.
DAP (Delivered at Place): Under this term, the seller is responsible for delivering the goods to a named place of destination, but the buyer is responsible for all costs and risks associated with the unloading and further transportation of the goods from that point.
DPU (Delivered at Place Unloaded): Under this term, the seller is responsible for delivering the goods to a named place of destination, and is responsible for unloading the goods at that point. The buyer is responsible for all further transportation costs and risks.
DDP (Delivered Duty Paid): Under this term, the seller is responsible for delivering the goods to a named place of destination, and is responsible for all costs and risks associated with the transportation of the goods to that point, including customs duties.
FAS (Free Alongside Ship): Under this term, the seller is responsible for delivering the goods alongside the vessel at a named port of shipment. The buyer is responsible for all further costs and risks associated with the goods from that point.
FOB (Free on Board): Under this term, the seller is responsible for delivering the goods onto the vessel at a named port of shipment. The buyer is responsible for all further costs and risks associated with the goods from that point.
CFR (Cost and Freight): Under this term, the seller is responsible for delivering the goods onto the vessel at a named port of shipment, and is responsible for the cost of transportation to the named port of destination.
CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight): Under this term, the seller is responsible for delivering the goods onto the vessel at a named port of shipment, and is responsible for the cost of transportation to the named port of destination, as well as insurance for the goods during transit.
Incoterms play an important role in international trade as they help to avoid misunderstandings between buyers and sellers, and provide a framework for allocating costs and risks. They also help to ensure that the parties involved in a transaction are clear on their responsibilities and obligations. However, it is important to note that the Incoterm should be agreed between the buyer and seller prior to shipping.


Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.